Why Are C-Section Rates Still Going Up?
Posted by Clark Venable on 3/8/2007
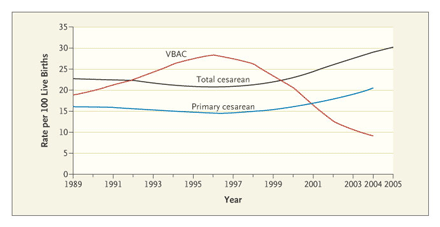
As an anesthesiologist I provide anesthesia for cesarean sections quite often. In fact, when I'm on overnight call it's what I spend most of my time doing. Usually, anesthesia for c-section consists of a spinal anesthetic, or using a pre-existing epidural catheter, or (more rarely and usually only in emergencies) a general anesthetic. I am therefore quite interested in the subject of cesarean section rates and what effects how often they are done. I learned some things from this article [free full text]:
Cesarean Delivery and The Risk-Benefit Calculus
1. Parturients are different--they are heavier and older.
2. The number of premature and low birth-weight babies has grown.
3. Vaginal breech deliveries are no longer recommended.
4. Operative deliveries (forceps or vacuum) are less common due to better data describing their risks.
5. More labors are induced (20% in 2003 vs 9.5% in 1990) and induced labors are more likely to result in C-section.
6. Changes in provider behavior
Look at John Edwards' list of law cases (thank you, Google). Notice the medical malpractice cases:
|
MEDICAL MALPRACTICE CASES Another specialty Edwards developed was in medical malpractice cases involving problems during births of babies. According to the New York Times, after Edwards won a $6.5M verdict for a baby born with cerbral-palsy, he filed at least 20 similar lawsuits against doctors and hospitals in deliveries gone wrong, winning verdicts and settlements of more than $60M. |
||||
| Case | Summary of Facts | Case Type | Result | |
| Griffin v. Teague, et al. (Mecklenburg Co. Superior Ct., NC, 1997) |
Application of abdominal pressure and delay in performing c-section caused brain damage to infant and resulted in child having cerebral palsy and spastic quadriplegia. Verdict set record for malpractice award. | Medical Malpractice | $23.25M verdict |
|
|
Campbell v. Pitt County Memorial Hosp. (Pitt County, NC, 1985) |
Infant born with cerebral palsy after breech birth via vaginal delivery, rather than cesarean. Established North Carolina precedent of physician and hospital liability for failing to determine if patient understood risks of particular procedure. | Medical Malpractice |
$5.75M settlement |
|
| Wiggs v. Glover, et al. | Plaintiff alleged infant's severe cerebral palsy was caused by negligent administration of pitocin, failure to use fetal monitor, or timely intervening in baby's fetal distress. | Medical Malpractice |
2.5M settlement |
|
| Cooper v. Craven Regional Med. Ctr., et al. | Infant suffered severe brain damage after obstetrician failed to moderate use of Picotin after baby displayed clear fetal distress. | Medical Malpractice |
$2.5M settlement |
|
| Dixon v. Pitt County Memorial Hospital (Pitt County, NC) |
Birth-related injuries including cerebral palsy and mental retardation allegedly caused by obstetrician's failure to diagnose fetal distress, including umbilical cord wrapped around baby's neck prior to delivery. | Medical Malpractice |
2.4M settlement |
|
Despite the increase in c-section rates nationwide, we have seen no reduction in the cerebral palsy rate...
This post has 0 replies
See full thread